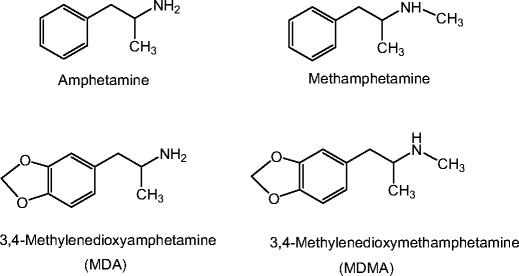
Related MDMA analogues
Many drugs containing amphetamine and its derivatives are synthesized in shadow laboratories. MDMA and MDA are considered the most common. Most ecstasy analogues are psychoactive amphetamine-type compounds that affect the central and peripheral adrenergic receptors. The general picture of poisoning is identical, but the manifestation of clinical features is possible.
MDMA analogues
MDMA is part of the phenylethylamine derivatives subgroup. The main compound in the drug is amphetamine or α–methylphenylethylamine. In shadow laboratories, hydrogen atoms are replaced. The result is a lot of new synthetic drugs.
The addition or modification of the chemical formula of amphetamine leads to the creation of a drug with an increased degree of effect on the central nervous system. Acute intoxication develops from the first application.
All amphetamine-type drugs are psychoactive compounds. After taking MDMA or its analogue, there is an impact on mental processes. Psychoactive compounds stimulate excessive synthesis of neurotransmitters and dopamine. The transport of serotonin into the nerve fiber is blocked, so psychomotor agitation occurs.
The chemical formula of MDMA is a substituted amphetamine. But ecstasy and its analogues, in addition to changes in the molecular structure, have high lipophilicity. The rate of penetration of metabolites through the blood-brain barrier into the central nervous system depends on it.
Amphetamine-type drugs quickly form psychological cravings and tolerance. The usual dose no longer causes the desired pharmacological effect. Increasing the dosage leads to acute poisoning.
An overdose of an amphetamine-type drug enhances all the pharmacological effects characteristic of adrenomimetics. Insomnia develops, paranoia increases, aggressiveness increases. Sometimes convulsions and violent convulsions develop, leading to death. Psychomotor agitation is similar to an acute attack of schizophrenia.
Inappropriate behavior of addicts due to drug intoxication or psychosis on the background of intoxication often leads to fatal accidents.
Amphetamine addiction has the highest tendency to increase the single and daily dose. The use of MDMA causes a sleep disorder, so the symptoms of acute psychosis are of the type of paranoid schizophrenia.

Structural analogues of MDMA:
mescaline;
norephedron;
amphetamine;
methamphetamine.
MDMA also has many analogues among other psychoactive compounds. Psychoactive substances have a heterogeneous chemical composition, but the mechanisms of action on the central nervous system are similar.
Tenamphetamine
MDA is a precursor to ecstasy. Both drugs belong to the same group of chemical compounds and are almost homologous in their structure. The clinical effects are similar, but tenamphetamine is twice as neurotoxic as MDMA.
MDA has a more powerful stimulating effect on the central nervous system, so psychosis can develop even after a single dose. Tolerance to tenamphetamine develops very quickly, and withdrawal syndrome proceeds in a severe form.
MDA is one of the first synthesized synthetic amphetamines. MDA was widely used in drug trafficking in America in the 60 – 70s and was known as Mellow pills or love pills. The popularity of MDA declined after numerous deaths in the United States and Canada, which were associated with the use of this substance. But this drug is still widely used in a number of European countries.
Ephedrine
Ephedrine is a synthetic psychostimulant. On the basis of benzene, which undergoes condensation with carboxylic acid chlorohydride, chloroethylphenyl ketone is obtained. After recovery, synthetic ephedrine is obtained. Taking the drug stimulates a powerful release of norepinephrine into the synaptic cleft.
Clinical effects after the use of ephedrine:
A sharp rise in HELL;
Tachycardia;
Suppression of intestinal motility;
Hypertonicity of skeletal muscles;
Increased concentration of glucose in the blood;
Physiological mydriasis;
Vascular stenosis;
Complete lack of appetite.
The medical use of ephedrine in many countries is considered unsafe, as drug dependence and cardiovascular pathologies develop. An oxidation product, ephedron, is used in illicit trafficking.
In comparison with the amphetamine series, ephedrine has a less pronounced psychostimulating effect, and the toxic effect is short-lived. But it is still used in shadow laboratories as an additional component, enhancing the psychostimulating effect of another drug.
Pervitin
Pervitin has been legally used in medicine for 50 years. The drug contained methamphetamine in its composition. Currently, psychotropic substances are obtained in an artisanal way.
In the slang of drug addicts, the resulting mixture is called “screw”. The composition of the drug includes various analogues of ephedrine and acid. Under the influence of high temperatures, amphetamine derivatives are formed in the mixture.
The psychostimulator forms a rapid mental dependence and tolerance. Artisanal pseudomethamphetamine has a long-lasting effect on the central nervous system. Psychomotor agitation can last for a day.
The “screw” has a devastating effect on blood vessels and neurons. A side effect in the form of cardiotoxic shock or psychosis may develop after a single use. Artisanal drug has many impurities, which causes secondary complications or diseases (abscesses, thrombosis, infections) to develop.
Mescaline
The psychotropic substance belongs to the group of phenylethylamines. The pharmacological effect and its duration are similar to MDMA.
Clinical effect:
Dizziness;
Vomiting;
Rapid heartbeat;
Chills turning into a feeling of heat;
Panic attacks;
Confusion of consciousness (inhibition, sopor);
Disorientation.
In underground laboratories, psychedelic drugs are synthesized from gallic acid or vanillin. Hydrochloride and mescaline sulfate have different pharmacological activity when using the same dosage.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine belongs to the amphetamine-type psychedelics. The psychostimulator consists of two enantiomers – right-rotating and left-rotating. The drug has a high neurotoxicity.
After taking the drug, the toxins quickly overcome the protective barrier of the brain – an adrenaline surge occurs. The metabolism of toxic substances in the body is slow, so the effect on the central nervous system takes a long time. Repeated dose intake leads to the accumulation of toxins in the tissues, which as a result leads to acute poisoning.
MDMA analogues
With chronic methamphetamine poisoning, addiction to the drug develops. This forces the addict to use the drug more often, because upon discontinuation of the drug withdrawal syndrome develops, which is characterized by the development of a directly opposite condition and directly opposite pharmacological effects.
Methylon
MDMS is an amphetamine–type drug. The psychostimulating effect is similar to MDMA. But, despite the similar pharmacological effect, MDMA and MDMS are not completely identical drugs.
Methylon stimulates the central nervous system somewhat less, but addiction and tolerance develop quite quickly. Adverse reactions and withdrawal stages are identical to MDMA.
Brolamphetamine
DOB is a phenylethylamine class drug. Drug addicts describe the effect of a psychedelic as: “an improved amphetamine version of LSD.” This is due to the prolonged effect of brolamphetamine (up to 30 hours).
The effect on mental processes is more similar to the predecessor of MDMA – MDA. But the intensity of the drug’s effect exceeds MDA by almost 100 times.
After taking the dose, there is a “blackout” – the surrounding reality is not felt, fainting is possible. Chronic drug addiction causes vasoconstriction of blood vessels, which as a result leads to the development of gangrene. DOB is often sold on the shadow market under the guise of ecstasy or mescaline.
Pharmacy analogues of MDMA
Shadow laboratories and drug addicts use many over-the-counter medications as a precursor, synthesizing various psychostimulants. By adding auxiliary components to the active substance, an “artisanal” psychedelic is obtained at the output.
But there is also pharmacy addiction. Addicts purchase affordable medicines. By repeatedly exceeding the therapeutic dosage, drug addicts get a psychotropic effect.
An artisanal mixture based on pharmacy raw materials often leads to an overdose, since it is impossible to calculate a “safe” dose. The lack of sterility during drug synthesis and a lot of difficult-to-dissolve impurities in the composition during intravenous administration causes toxic shock (sepsis) and the development of necrotic foci in organs.
MDMA analogues:
Zestra – the composition includes pseudoephedrine. Uncontrolled use of the drug leads to psychophysiological dependence. Drug addicts use the drug as a raw material to create a “screw”;
Medicines for the treatment of dry cough and relief of asthma attacks (Bronchoton, Broncholitin, Broncholitin, Bronchitusen, Bronchocin) – ephedrine is included in the composition. Overdose of drugs causes tachycardia and various cognitive disorders;
Sulfocamphocaine is an analeptic. In shadow laboratories, they are used as an additional component, enhancing the psychostimulating effect of the drug. Tolerance to the drug is rapidly developing;
Tramadol – despite the opioid profile also has a stimulating effect.
Conclusion
MDMA has a large number of analogues.
MDA and DOB exceed MDMA in clinical effect.
MDMA has pharmacy analogues.
