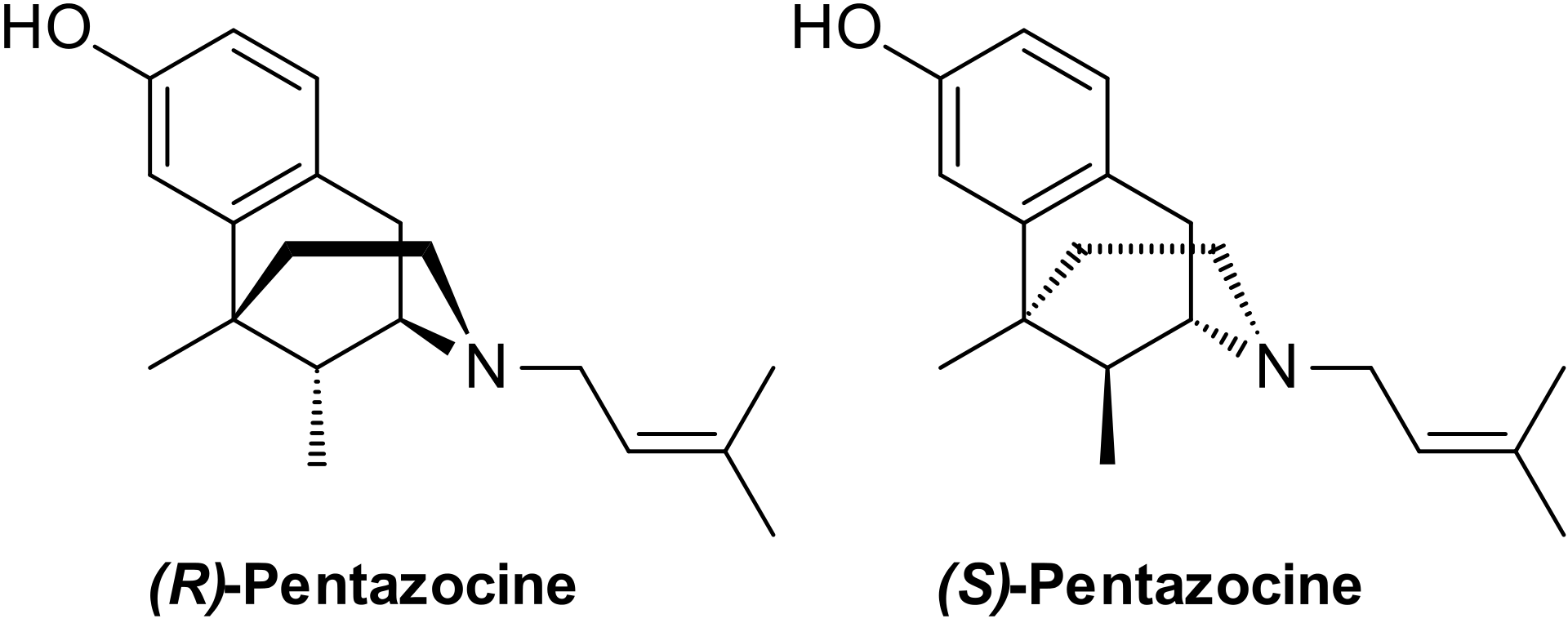
Pentazocin(Talvin)
Pentazocyndrug names: talvin, fortral, lexir.
An attempt to find an effective painkiller that does not cause addiction led to the creation of pentazocin (talvin). Introduced in 1967 as an analgesic, it quickly appeared on the illegal market, usually in combination with tripennamine. The list of narcotic drugs subject to control in the Russian Federation is in list II. An attempt to lower the level of use of this drug was made with the introduction of Talvin Nx. This product contains a certain amount of a counteracting substance to neutralize effects similar to morphine, if the tablets are dissolved and then taken orally.
Pentazocin is a synthetic opioid from the benzomorphan group. Its analgesic properties are associated with the levorotatory isomer of this drug.
Pentazocin causes respiratory depression. Among mixed agonist-antagonists, it has the maximum ability to suppress breathing and cause analgesia. When the dose of the drug is higher than 30 mg, there is no proportional increase in respiratory depression. In an adult with a body weight of 70 kg, the maximum effect occurs at a dose of 60 mg. Pentazocin does not cause hypotension and bradycardia, however, there is evidence of a moderate hyperdynamic effect with intravenous administration of 30 mg (increased blood pressure and pressure in the small circle, tachycardia). The effect of pentazocin on the pressure in the biliary tract is weakly expressed. The danger of developing addiction is small, but sometimes physical dependence and drug addiction appear. Pentazocin is able to accelerate the development of withdrawal syndrome in people with physical dependence on opioids.
Pentazocine lactate is released in a solution for injection at a concentration of 30 mg / ml. for oral administration, they are released in tablets with acetylsalicylic acid (12.5 mg pentazocin and 325 mg acetylsalicylic acid) or with naloxone (50 mg pentazocin and 0.5 mg naloxone). The dose of pentazocin for adults is 30 mg / m or 50 mg every 3-4 hours enterally. At a dose of 50 mg, pentazocin has an analgesic effect equivalent to 60 mg of codeine.
Pharmacokinetics
Pentazocin is well absorbed with enteral and parenteral administration. After oral administration, the biological effect has no more than 20% of the administered dose of the drug due to intensive metabolism in the liver.
During metabolism, inactive glucuronides are formed, which are excreted in the urine together with 5-25% of the unchanged drug.
Pharmacological action
Pentazocin causes analgesia as well as psychomimetic and dysphoric effects.
With parenteral administration, pentazocin is 2-3 times weaker than morphine. The drug also causes sedation and sweating. High doses of pentazocin provoke hallucinations and psychomimetic effect (“active anxiety”, depersonalization, etc.).
Pentazocin causes respiratory depression.Among mixed agonist-antagonists, it has the maximum ability to suppress breathing and cause analgesia. When the dose of the drug is higher than 30 mg, there is no proportional increase in respiratory depression. In an adult with a body weight of 70 kg, the maximum effect occurs at a dose of 60 mg. Pentazocin does not cause hypotension and bradycardia, however, there is evidence of a moderate hyperdynamic effect with intravenous administration of 30 mg (increased blood pressure and pressure in the small circle, tachycardia). The effect of pentazocin on the pressure in the biliary tract is weakly expressed. The danger of developing addiction is small, but sometimes physical dependence and drug addiction appear. Pentazocin is able to accelerate the development of withdrawal syndrome in people with physical dependence on opioids.
Among mixed agonist-antagonists, it has the maximum ability to suppress breathing and cause analgesia. When the dose of the drug is higher than 30 mg, there is no proportional increase in respiratory depression.
In an adult with a body weight of 70 kg, the maximum effect occurs at a dose of 60 mg.
The danger of developing addiction is small, but sometimes physical dependence and drug addiction appear. Pentazocin is able to accelerate the development of withdrawal syndrome in people with physical dependence on opioids.
Use in the clinic
Pentazocin can be used as an antagonist of morphine (fentanyl). The administration is carried out 10-15 minutes before the end of the operation: pentazocin (1 mg / kg) is injected slowly (for 2-3 minutes); it is advisable to first introduce half of the calculated dose, and after 3-4 minutes – the remaining part.
The effect of awakening and restoring independent breathing occurs after 3-4 minutes. Reducing respiratory depression associated with the use of fentanyl, pentazocin with intravenous administration itself leads to it, although the duration of depression is much shorter.
The dose of pentazocin for adults is 30 mg / m or 50 mg every 3-4 hours enterally. At a dose of 50 mg, pentazocin has an analgesic effect equivalent to 60 mg of codeine.
