Antidepressants
Antidepressants combine a large group of drugs, the main property of which is the elimination of a depressive state. Antidepressants include MAO inhibitors: hydrazine (iprazide, nialamide) and nonhydrazine derivatives (indopan, etc.), 4- and 3-cyclic compounds (mianserin, imipramine, amitriptyline, azafen, pyrazidol), secondary amines (desipramine).
There is also a group of antidepressants of the second generation (nomifenzyl, trazadone, etc.) and lithium preparations.
Possible side effects: drowsiness, dry mouth, “shroud” in front of the eyes, constipation, difficulty urinating, fainting, sweating, trembling, rash, palpitations, headache.
A warning: In combination with certain medications and foods, MAO inhibitors have the opposite effect, which can lead to a significant increase in blood pressure.
When using antidepressants of both groups, alcohol intake should be limited. Ask your doctor if it is possible to drive a car or other mechanisms while taking antidepressants.
Additional information
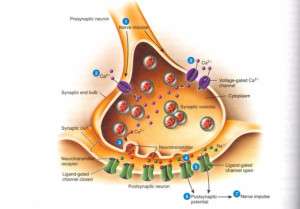
Tricyclic compounds are the most studied and safe. The mechanism of action of tricyclic antidepressants is associated with the blockade of the reuptake of norepinephrine by presynaptic nerve endings, as a result of which the content of norepinephrine in synaptic slits increases.
In the places of accumulation of norepinephrine (various structures of the brain, as well as the heart and lungs, spleen and other organs), the activity of adrenergic transmission of nerve impulses increases, central and peripheral a- and b-adrenergic receptors are excited.
A similar effect of 3-cyclic antidepressants is observed with respect to dopamine and serotonin. Drugs of this group block central and peripheral M-cholinergic receptors, exerting an atropine-like effect.
MAO inhibitors nialamide block monoamine oxidase, which causes oxidative deamination and inactivation of monoamines (norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin) with the accumulation of these amines in the structures of the brain.
Some antidepressants combine the action of MAO inhibitors and 4- and 3-cyclic compounds. A common property of all antidepressants is a timoleptic effect: influence on the affective sphere with an improvement in mood and general mental state.
Description of antidepressants:
Melipramine (imizine, antideprin, imipramine) refers to strong antidepressants with concomitant stimulating effect.
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is well absorbed when taken orally, reaches its maximum concentration in the blood after 1-2 hours, after intramuscular administration – after 30-60 minutes. It accumulates in the liver, kidneys, and brain. It penetrates well through the blood-brain barrier. The protein bond is 76-95%. It is actively metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine. The half-life is 9-20 hours. Indications. Melipramine is used for depressive conditions of various etiologies: astheno-depressive states, endogenous depression in patients with manic-depressive psychosis, reactive depression, depressive states in psychopathies, neuroses, as well as enuresis.
The antidepressant effect develops gradually, after 1-2 weeks. Melancholy decreases, motor inhibition improves, mood improves, cheerfulness appears, and the mental and general tone of the body increases. If there is no effect for 2-3 weeks, the drug is canceled. The course of treatment is 4-5 weeks.
Side effects.
With hypersensitivity or overdose, insomnia, agitation, anxiety, hallucinations, and delirium may increase or appear. The drug is canceled and neuroleptics are prescribed, with insomnia – sleeping pills. In some cases, headache, dizziness, tremor, sweating, numbness of the extremities, paresthesia, collapse, itching, allergic reactions, leukocytosis, eosinophilia are noted. Due to the cholinolytic effect, dry mouth, impaired accommodation, urinary retention, tachycardia, dyspeptic disorders are possible.
Contraindications
Acute diseases of the liver, kidneys, hematopoietic organs, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular insufficiency, cardiac conduction disorders, infectious diseases, cerebral circulatory disorders, glaucoma, prostate adenoma, bladder atony, the first trimester of pregnancy. Oral administration is contraindicated in peptic ulcer disease.
Amitriptyline (tryptisol) It also refers to drugs with good bioavailability and high affinity for plasma protein. The half-life in healthy people is 24-48 hours, and in patients it ranges from 9 to 24 hours. The therapeutic concentration of amitriptyline in the blood is 0.04-0.16 mcg/ml. The drug is actively metabolized in the liver, turning into nor- and dinitrotriptyline, which have antidepressant properties. These two metabolites, as well as hydroxyl compounds and N-oxides, are excreted in the urine: in 2 weeks, 80% of the metabolites are excreted in this way.
The main indication for the use of antidepressants, taking into account the peculiarities of their pharmacodynamics, are depressive states. For depressive conditions accompanied by lethargy, lethargy, lack of initiative, nialamide 50-70 mg / day is used in the morning and afternoon.
The therapeutic effect is usually restored after 1-2 weeks of administration. Nialamide is also used for trigeminal neuralgia, angina pectoris. The interaction of MAO inhibitors with a significant number of drugs, as well as products containing tyramine and phenylethylene (cheese, coffee, beer, wine, cream), with the development of severe complications limits the use of drugs in this group.
Differences in the indications for the use of other antidepressants.
Imizin with an antidepressant effect has the effect of primotor and ideatory inhibition, involutive, menopausal, reactive, alcoholic depression. At the same time, the feeling of longing disappears, the mood improves, cheerfulness appears, and motor retardation decreases. It is prescribed orally at a dose of 75-100 mg / day with a gradual increase to 200-250 mg / day. Children under 1 year old (and the elderly) receive a dose of 100 mg / day, which is doubled every 7 years of life.
Amitriptyline is prescribed for the same indications starting from 50-75 mg / day.
Azafen is used for mild and moderate depression, including widespread use in outpatient practice at a dose of 25-50 mg / day with a gradual increase to 150-200 mg / day. Azafen has a weak hypnotic effect and, unlike imizine and amitriptyline, is devoid of cholinolytic activity, and therefore can be used in patients with glaucoma and prostate adenoma, in the elderly.
Pyrazidol (pirlindol) has the properties of MAO inhibitors and 3- and 4-cyclic compounds. It is used for manic-depressive psychoses, schizophrenia with affective disorders, infolution psychoses and other pathological conditions.
